Highlights
-
Systematic study of cluster radioactivity in trans-lead nuclei with various versions of proximity potential formalisms
2024, 48(5): 054101. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ad260b
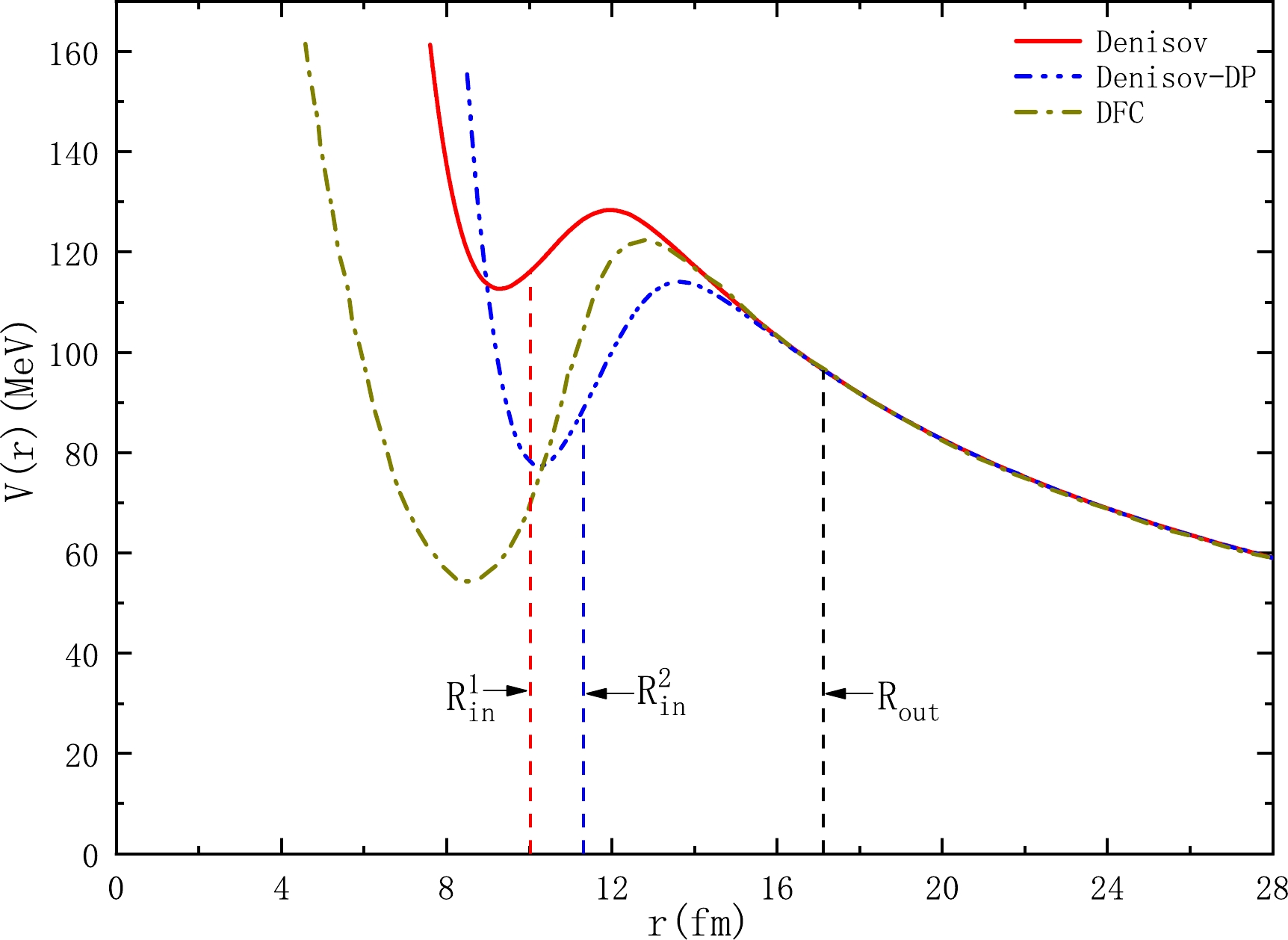 In this study, based on the framework of the Coulomb and proximity potential model (CPPM), we systematically investigate the cluster radioactivity half-lives of 26 trans-lead nuclei by considering the cluster preformation probability, which possesses a simple mass dependence on the emitted cluster according to R. Blendowske and H. Walliser [Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 1930 (1988)]. Moreover, we investigate 28 different versions of the proximity potential formalisms, which are the most complete known proximity potential formalisms proposed to describe proton radioactivity, two-proton radioactivity, α decay, heavy-ion radioactivity, quasi-elastic scattering, fusion reactions, and other applications. The calculated results show that the modified forms of proximity potential 1977, denoted as Prox.77-12, and proximity potential 1981, denoted as Prox.81, are the most appropriate proximity potential formalisms for the study of cluster radioactivity, as the root-mean-square deviation between experimental data and relevant theoretical results obtained is the least; both values are 0.681. For comparison, the universal decay law (UDL) proposed by Qi et al. [Phys. Rev. C 80, 044326 (2009)], unified formula of half-lives for α decay and cluster radioactivity proposed by Ni et al. [Phys. Rev. C 78, 044310 (2008)], and scaling law (SL) in cluster radioactivity proposed by Horoi et al. [J. Phys. G 30, 945 (2004)] are also used. In addition, utilizing CPPM with Prox.77-12, Prox.77-1, Prox.77-2, and Prox.81, we predict the half-lives of 51 potential cluster radioactive candidates whose cluster radioactivity is energetically allowed or observed but not yet quantified in NUBASE2020. The predicted results are in the same order of magnitude as those obtained using the compared semi-empirical and/or empirical formulae. At the same time, the competition between α decay and cluster radioactivity of these predicted nuclei is discussed. By comparing the half-lives, this study reveals that α decay predominates.
In this study, based on the framework of the Coulomb and proximity potential model (CPPM), we systematically investigate the cluster radioactivity half-lives of 26 trans-lead nuclei by considering the cluster preformation probability, which possesses a simple mass dependence on the emitted cluster according to R. Blendowske and H. Walliser [Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 1930 (1988)]. Moreover, we investigate 28 different versions of the proximity potential formalisms, which are the most complete known proximity potential formalisms proposed to describe proton radioactivity, two-proton radioactivity, α decay, heavy-ion radioactivity, quasi-elastic scattering, fusion reactions, and other applications. The calculated results show that the modified forms of proximity potential 1977, denoted as Prox.77-12, and proximity potential 1981, denoted as Prox.81, are the most appropriate proximity potential formalisms for the study of cluster radioactivity, as the root-mean-square deviation between experimental data and relevant theoretical results obtained is the least; both values are 0.681. For comparison, the universal decay law (UDL) proposed by Qi et al. [Phys. Rev. C 80, 044326 (2009)], unified formula of half-lives for α decay and cluster radioactivity proposed by Ni et al. [Phys. Rev. C 78, 044310 (2008)], and scaling law (SL) in cluster radioactivity proposed by Horoi et al. [J. Phys. G 30, 945 (2004)] are also used. In addition, utilizing CPPM with Prox.77-12, Prox.77-1, Prox.77-2, and Prox.81, we predict the half-lives of 51 potential cluster radioactive candidates whose cluster radioactivity is energetically allowed or observed but not yet quantified in NUBASE2020. The predicted results are in the same order of magnitude as those obtained using the compared semi-empirical and/or empirical formulae. At the same time, the competition between α decay and cluster radioactivity of these predicted nuclei is discussed. By comparing the half-lives, this study reveals that α decay predominates. -
Strong decays of the Pc(4312) and its isospin cousin via the QCD sum rules
2024, 48(5): 053102. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ad2442
 In this study, considering the conservation of isospin in the strong decays, we investigate the strong decays of the pentaquark molecule candidate
In this study, considering the conservation of isospin in the strong decays, we investigate the strong decays of the pentaquark molecule candidate$ P_c(4312) $ and its possible higher isospin cousin$ P_c(4330) $ in the framework of the QCD sum rules. Further, the pole residue of the Δ baryon with isospin eigenstate$ |II_3\rangle=|\frac{3}{2}\frac{1}{2}\rangle $ is obtained. If the possible pentaquark molecule candidate$ P_c(4330) $ could be determined, it would shed light on the interpretations of the$ P_c $ states in future experiments. -
B meson rare decays in the TNMSSM
2024, 48(5): 053104. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ad2a62
 We investigate the two loop electroweak corrections to B meson rare decays
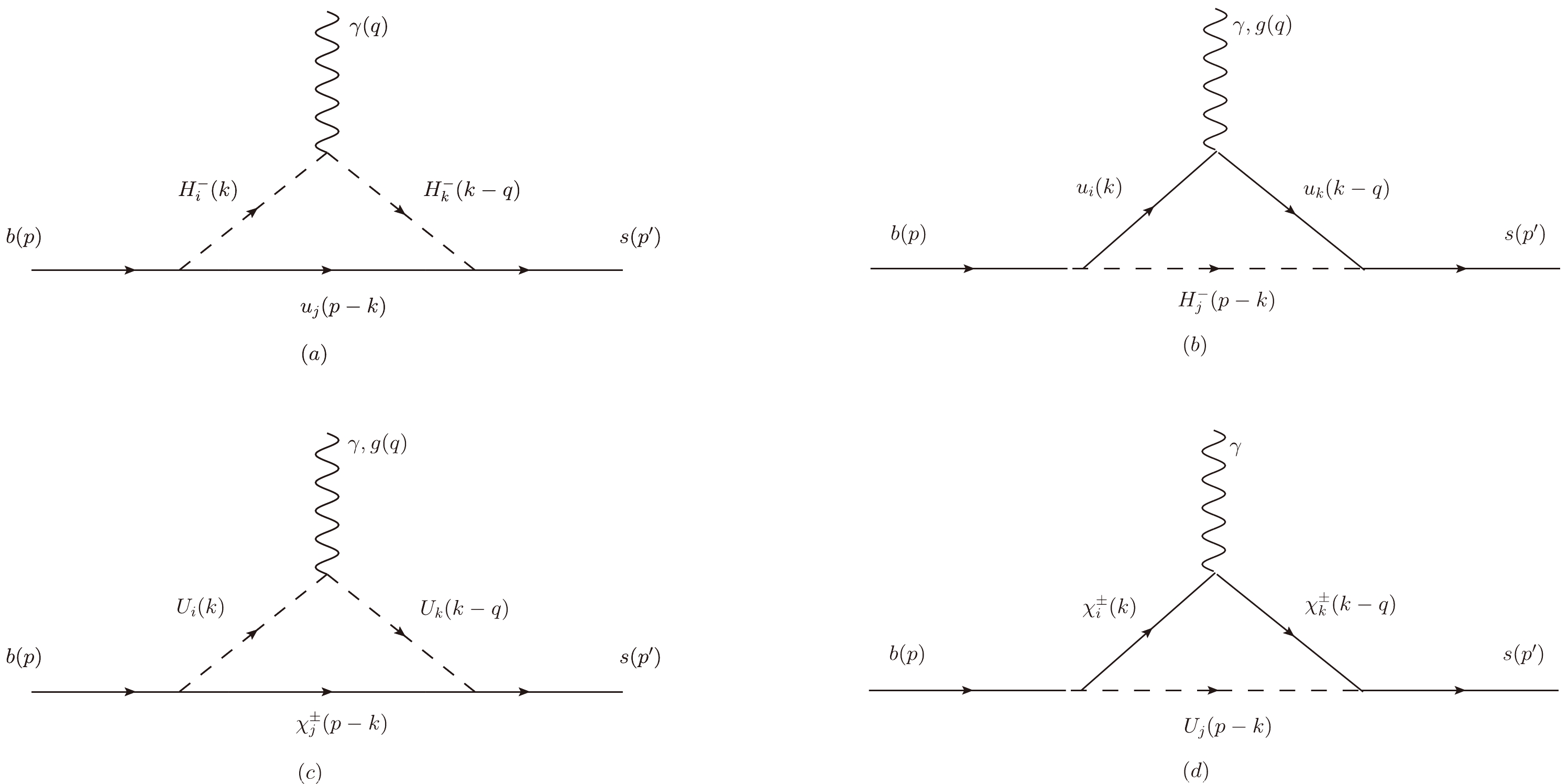
We investigate the two loop electroweak corrections to B meson rare decays$ \bar B\rightarrow X_s\gamma $ and$ B_s^0\rightarrow \mu^+\mu^- $ in the minimal supersymmetry standard model (MSSM) extension with two triplets and one singlet (TNMSSM). The new particle contents and interactions in the TNMSSM can affect the theoretical predictions of the branching ratios$ {\rm{Br}}(\bar B\rightarrow X_s\gamma) $ and$ {\rm{Br}}(B_s^0\rightarrow \mu^+\mu^-) $ , and the corrections from two loop diagrams to the process$ \bar B\rightarrow X_s\gamma $ can reach around$ 4\% $ . Considering the latest experimental measurements, the numerical results of$ {\rm{Br}}(\bar B\rightarrow X_s\gamma) $ and$ {\rm{Br}}(B_s^0\rightarrow \mu^+\mu^-) $ in the TNMSSM are presented and analyzed. The findings indicate that the results in the TNMSSM can fit the updated experimental data well, and the new parameters$ T_{\lambda},\;\kappa,\;\lambda $ , clearly affect the theoretical predictions of$ {\rm{Br}}(\bar B\rightarrow X_s\gamma) $ and$ {\rm{Br}}(B_s^0\rightarrow \mu^+\mu^-) $ .
Just Accepted
More >
-
A 95 GeV light Higgs in the top-pair-associated diphoton channel at the LHC in the Minimal Dilaton Model
Published: 2024-04-29
-
Systematic investigation of nucleon optical model potentials in (p, d) transfer reactions
Published: 2024-04-29
-
Periapsis shift in spherically symmetric spacetimes and effect of electric interaction
Published: 2024-04-28
Recent
More >
-
Surface growth approach for bulk reconstruction in the AdS/BCFT correspondence
2024, 48(6): 065106-065106-10. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ad32beShow AbstractIn this study, we extend the surface growth approach for bulk reconstruction into the AdS spacetime with a boundary in the AdS/BCFT correspondence. We show that the geometry in the entanglement wedge with a boundary can be constructed from the direct growth of bulk extremal surfaces layer by layer. Furthermore, we observe that the surface growth configuration in BCFT can be connected with the defect multi scale entanglement renormalization ansatz (MERA) tensor network. Additionally, we investigate the entanglement of purification within the surface growth process, which not only reveals more refined structure of entanglement entropy in the entanglement wedge but also suggests a selection rule for surface growth in the bulk reconstruction.
-
A study of U-isotope ground state properties with covariant energy density functional
2024, 48(6): 064102-064102-6. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ad305cShow AbstractIn this study, we systematically analyzed the ground state of uranium isotopes from 225 to 240. In our calculations, we used the covariant energy density functional of density-dependent meson exchange interaction (DD-ME2) with separable pairing interaction (TMR). Using the multiple deformation constraint, we calculated the potential energy surface (PES) of the uranium isotopes for both even-even and even-odd nuclei with quadrupole and octupole deformation. Based on our calculation and upon comparing the experimental data and Hartree-Fock-Bogoliubov calculations with Gogny D1S calculation data, the ground state of uranium isotopes with reflection-asymmetric deformation was found to be preferred.
-
Constraints on axion-like particles from the observation of Galactic sources by the LHAASO
2024, 48(6): 065107-065107-8. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/ad361eShow AbstractHigh-energy photons may oscillate with axion-like particles (ALPs) when they propagate through the Milky Way's magnetic field, resulting in an alteration in the observed photon energy spectrum. Ultra-high energy gamma-ray spectra, measured by the Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) up to
$ {\cal{O}}(1)\; {\rm{PeV}} $ , provide a promising opportunity to investigate the ALP-photon oscillation effect. In this study, we utilize the gamma-ray spectra of four Galactic sources measured by the LHAASO, that is, the Crab Nebula, LHAASO J2226+6057, LHAASO J1908+0621, and LHAASO J1825-1326, to explore this effect. We employ the CLs method to set constraints on the ALP parameters. Our analysis of the observations of the four sources reveals that the ALP-photon coupling$ g_{a\gamma} $ is constrained to be smaller than$ 1.4\times 10^{-10} $ $ {\rm GeV}^{-1} $ for an ALP mass of$ \sim 4\times 10^{-7} \; {\rm{eV}} $ at 95% C.L. Combining the observations of the Crab Nebula from the LHAASO and other experiments, we find that the ALP-photon coupling may be set to approximately$ 7.5\times 10^{-11} $ $ {\rm GeV}^{-1} $ for an ALP mass of$ \sim 4 \times 10^{-7}\; {\rm{eV}} $ , which is similar to the CAST constraint.
Archive
ISSN 1674-1137 CN 11-5641/O4
Original research articles, Ietters and reviews Covering theory and experiments in the fieids of
- Particle physics
- Nuclear physics
- Particle and nuclear astrophysics
- Cosmology
Author benefits
- A SCOAP3 participating journal - free Open Access publication for qualifying articles
- Average 24 days to first decision
- Fast-track publication for selected articles
- Subscriptions at over 3000 institutions worldwide
- Free English editing on all accepted articles
News
- Chinese Physics C Outstanding Reviewer Award 2023
- Impact factor of Chinese Physics C is 3.6 in 2022
- 2022 CPC Outstanding Reviewer Awards
- The 2023 Chinese New Year-Office closure
- 《Chinese Physics C》BEST PAPER AWARDS 2022
Cover Story
- Cover Story (Issue 4, 2024) | Advancing gravitational wave astronomy: AI-enhanced detection and real-time analysis in the presence of glitches
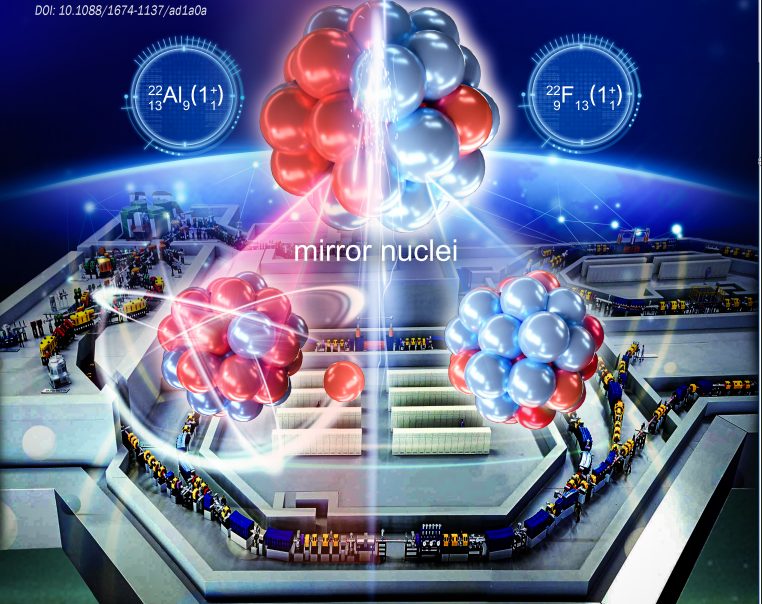
- Cover Story (Issue 3, 2024) | First measurement of the ground-state mass of 22Al helpsto evaluate the ab-initio theory
- Cover Story (Issue 2, 2024) | Quark/gluon taggers light the way to new physics
- Cover story (Issue 6, 2023) |Joint constraints on cosmological parameters using future multi-band gravitational wave standard siren observations
- Cover Story (Issue 5, 2023) | Production and decay of polarized hyperon-antihyperon pairs